Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Si
Si O
O
Suzuki, Eriko; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko; Oishi, Yuji*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Kurosaki, Ken*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(7), p.852 - 857, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.4(Nuclear Science & Technology)The low temperature heat capacity of Cs Si
Si O
O , which is one of the cesium chemisorbed compounds onto stainless steel during severe accident of the light water nuclear reactor, was experimentally determined for the first time in the temperature range of 1.9 - 302 K. The experimentally determined heat capacity,
, which is one of the cesium chemisorbed compounds onto stainless steel during severe accident of the light water nuclear reactor, was experimentally determined for the first time in the temperature range of 1.9 - 302 K. The experimentally determined heat capacity, 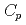
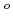 (298.15K), and the standard entropy,
(298.15K), and the standard entropy, 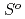 (298.15K), were 249.4
(298.15K), were 249.4  1.1 J K
1.1 J K mol
mol and 322.1
and 322.1  1.3 J K
1.3 J K mol
mol , respectively. The standard Gibbs energy of formation of Cs
, respectively. The standard Gibbs energy of formation of Cs Si
Si O
O at high temperatures,
at high temperatures, 

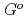 (
( ), were reevaluated by using the presently obtained
), were reevaluated by using the presently obtained 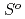 (298.15K) and the previously reported experimental results of the standard enthalpy of formation,
(298.15K) and the previously reported experimental results of the standard enthalpy of formation, 

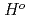 (298.15K), and the standard enthalpy increments at high temperatures,
(298.15K), and the standard enthalpy increments at high temperatures, 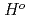 (
( )-
)-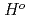 (298.15K).
(298.15K).
 C
CFukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nuclear Technology, 205(9), p.1154 - 1163, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:97.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)An electromagnetic-levitation technique performed in a static magnetic field was used to measure the density, surface tension, normal spectral emissivity, heat capacity, and thermal conductivity of molten 316L stainless steel (SS316L) and SS316L that contained 5mass%B C. The addition of 5mass%B
C. The addition of 5mass%B C to SS316L yielded reductions of 111 K, 6%, 19%, and 6% in the liquidus temperature, density, normal spectral emissivity, and thermal conductivity at the liquidus temperature of SS316L, respectively. The heat capacity increased by 5% with this addition. Although the 5mass%B
C to SS316L yielded reductions of 111 K, 6%, 19%, and 6% in the liquidus temperature, density, normal spectral emissivity, and thermal conductivity at the liquidus temperature of SS316L, respectively. The heat capacity increased by 5% with this addition. Although the 5mass%B C addition had no clear effect on the surface tension, sulfur dissolved in the SS316L resulted in a significant decrease in the surface tension.
C addition had no clear effect on the surface tension, sulfur dissolved in the SS316L resulted in a significant decrease in the surface tension.
 TiO
TiO added with TiO
added with TiO
Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Takeshi*; Nashimoto, Makoto*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Dokiya, Masayuki*; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*; Takahashi, Yoichi*
JAERI-Conf 2004-012, p.140 - 147, 2004/07
no abstracts in English
 TiO
TiO
Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Takeshi*; Nashimoto, Makoto*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*; Takahashi, Yoichi*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, Supplement, Vol.112, No.1 (CD-ROM), p.S354 - S357, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Shirasu, Yoshiro; Minato, Kazuo
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 337(1-2), p.243 - 247, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.88(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 Pu
Pu )TiO
)TiO (x=0 and 0.20)
(x=0 and 0.20)Sato, Tsuyoshi*; Yamazaki, Satoshi*; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Matsui, Tsuneo*; Nagasaki, Takanori*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 294(1-2), p.135 - 140, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; ; *; Yamaguchi, Akira
JNC TN9400 2000-109, 96 Pages, 2000/11
Numerical calculations were carried out for a free surface sloshing, a thermal stratification, a thermal striping, and a natural convection as key phenomena of in-vessel thermohydraulics in future fast reactor systems with various fluids as coolants. This numerical work was initiaied based on a recognition that the fundamental characteristics of the phenomena have been unsolved quantitatively in the use of various coolants. From the analysis for the phenomena, the following results were obtained. [Free Surface Sloshing phenomena] (1)Ther is no remarkable difference betweeen liquid sodium and luquid Pb-Bi in characteristics of internal flows and free surface charatristics based on Fr number. (2)the AQUA-VOF code has a potentiall enough to evaluate gas entrainment behavior from the free surface including the internal flow characteristics. [thermal Stratification Phenomena] (1)On-set position of thermal entainment process due to dynamic vortex flows was moved to downstream direction with decreasing of Ri number. 0n the other hand, the position in the case of C0 gas was shifted to upstream side with decreasing of Ri number. (2)Destruction speed of the thermal stratyification interface was dependent on thermal diffusivity as fluid properties. therefor it was concluded that an elimination method is necessary for the interface generated in C0
gas was shifted to upstream side with decreasing of Ri number. (2)Destruction speed of the thermal stratyification interface was dependent on thermal diffusivity as fluid properties. therefor it was concluded that an elimination method is necessary for the interface generated in C0 gas. [thermal Striping Phenomena] (1)Large amplitudes of fluid temperature fluctuations was reached to down stream area in the use of CO
gas. [thermal Striping Phenomena] (1)Large amplitudes of fluid temperature fluctuations was reached to down stream area in the use of CO gas, due to larger fluid viscosity and smaller thermal diffusivity, compared with liquid sodium and liquid Pb-Bi cases. (2)To simulate thermal striping conditions such as amplitude and frequency of the fluid temperature fluctuations, it isnecessary for coincidences of Re number for the amplitude and of velocity value for the frequency, in various coolants. [Natural Convection Phenomena] (1)Fundamental behavior of the natural convection in various coolant follows buoyant jet ....
gas, due to larger fluid viscosity and smaller thermal diffusivity, compared with liquid sodium and liquid Pb-Bi cases. (2)To simulate thermal striping conditions such as amplitude and frequency of the fluid temperature fluctuations, it isnecessary for coincidences of Re number for the amplitude and of velocity value for the frequency, in various coolants. [Natural Convection Phenomena] (1)Fundamental behavior of the natural convection in various coolant follows buoyant jet ....
Arai, Yasuo; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Yasufumi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 271-273, p.602 - 605, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:67.98(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Yasufumi; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 271-273, p.577 - 582, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:85.49(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
*; Kyoya, Masahiko; *; *
JAERI-M 91-021, 61 Pages, 1991/03
no abstracts in English
Matsui, Tsuneo*; *; *; Imai, Hisashi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 186, p.7 - 12, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:78.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
*; *
PNC TN9410 88-130, 118 Pages, 1988/10
In the Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) of Monju, annual frequency of core damage was evaluated by the systems analysis for each accident category. Common mode or cause failure to open the stop valves of Auxiliary Cooling System (ACS) was found to be the most dominant contributor to the core damage frequency caused by Protected-Loss-Of-Heat-Sink (PLOHS) accidents. In this study, possibility of the recovery from the PLOHS condition by opening bypass valves has been investigated using Loop version of Super System Code (SSC-L). The bypass valve is located in parallel to the stop valve of ACS. Success criterion for the recovery has been proposed and general characteristics of the natural circulation decay heat removal have been pointed out. 0pening of the bypass valve in more than two loops is the proposed criterion for the successful decay heat removal by natural circulation. Based on a sensitivity analysis, it has been found that the grace time for the recovery action is sufficiently long. Upper bound of the pressure loss coefficient of the bypass valve has been also selected as a parameter for the sensitivity analysis to check the certainty of the conclusion. It has been found that the conclusion is supported within the uncertainty range of the pressure loss coefficient. In the situations where the stop valves are opened successfully, the decay heat can be removed by one loop natural circulation. Furthermore, the maximum coolant temperature reduces considerably by taking into account the mass heat capacity of the remaining two loops. The decay heat removal characteristics in the natural circulation mode are summarized as follows: (1)As the number of available heat transport loops lessens, the mass flow rate and heat removal capability per loop decreases. (2)The maximum coolant temperature is sensitive to the mass heat capacity of the plant system. Therefore, availability of the fluid and structural mass heat capacity should be investigated carefully ...
*; ; *; Okamoto, Yoshizo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 15(8), p.557 - 561, 1973/08
no abstracts in English
 C-SS eutectic molten material
C-SS eutectic molten materialHigashi, Hideo*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
To develop thermosphysical property model to simulate eutectic reaction behavior of B C as control rod material and stainless steel (SS) in core disruptive accident of sodium-cooled fast reactor, this paper reports measurement results of emissivity, heat capacity and thermal conductivity of 10mass%B
C as control rod material and stainless steel (SS) in core disruptive accident of sodium-cooled fast reactor, this paper reports measurement results of emissivity, heat capacity and thermal conductivity of 10mass%B C-SS melt by noncontact laser modulation calorimetry with very high temperature physical property measurement system (PROSPECT).
C-SS melt by noncontact laser modulation calorimetry with very high temperature physical property measurement system (PROSPECT).
Sasada, Yuto*; Miyazaki, Yuji*; Nakano, Motohiro*; Matsuo, Yusuke*; Walker, C.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
no journal, ,
Cementitous materials are to be used in large quantities in the geological disposal of highly radioactive TRU waste. Thermodynamic data on cement hydrate minerals are important to model the long-term dissolution behavior of cement materials during the reaction of these materials with groundwater. Portlandite (Ca(OH) ) is a major component (20 to 25 wt%) of hydrated Portland cement. Low temperature heat capacity measurements of three types of portlandite (low purity, high purity, and large crystal) showed purity dependence. The large crystal sample followed Debye's T
) is a major component (20 to 25 wt%) of hydrated Portland cement. Low temperature heat capacity measurements of three types of portlandite (low purity, high purity, and large crystal) showed purity dependence. The large crystal sample followed Debye's T rule at low temperatures, while the high and low purity samples showed upturn of heat capacity, possibly due to difference in absorbed water vapor and/or calcite (CaCO
rule at low temperatures, while the high and low purity samples showed upturn of heat capacity, possibly due to difference in absorbed water vapor and/or calcite (CaCO ) contamination. Heat capacities of the cement hydrates (ettringite:Ca
) contamination. Heat capacities of the cement hydrates (ettringite:Ca (Al(OH)
(Al(OH) )
) (SO
(SO )
) (H
(H O)
O) and monosulfate:Ca
and monosulfate:Ca Al
Al (OH)
(OH) (SO
(SO )(H
)(H O)
O) ) exhibited phase transitions associated with the hydration water.
) exhibited phase transitions associated with the hydration water.